跟骨骨折髓内钉内固定
时间:2021-10-09 19:01:52 热度:37.1℃ 作者:网络
累及后关节面的跟骨骨折需采用手术治疗已经达成共识,传统外侧“L”型扩大入路切口手术后切口并发症较多,随着技术的发展,现已发展出经跗骨窦入路、关节镜辅助复位等技术。
考虑跟骨内松质骨结构,并避免对骨膜及软组织血运造成破坏,有学者创新性采用髓内钉治疗跟骨骨折,并做了系列病例报告,取得良好的治疗效果。


一、Introduction
由于继发的距下关节病变和后足的形态变化,移位的跟骨关节内骨折非手术治疗通常与不良结局相关。因此,有人认为只有对关节面和跟骨的形状进行解剖学重建才能获得更好的长期效果,大多数外科医生现在都赞成外科治疗。
在很长一段时间内,治疗跟骨关节内骨折的金标准是通过扩大外侧入路进行切开复位内固定。然而,这种方法经常与伤口愈合并发症(5.8%-43%)相关,包括血肿、伤口浅表坏死、浅表和深部伤口感染。为了降低这些风险,在过去几年内,微创技术得到了很好的发展,包括经皮螺钉固定、经跗骨窦入路、有限后路和关节镜辅助固定。经跗骨窦入路可直接控制关节复位,无需广泛的软组织解剖,并结合经皮内固定,使软组织并发症发生率较低。在这项研究中,我们旨在评估经跗骨窦入路经皮螺钉固定移位的跟骨关节内骨折的疗效。
(Nonsurgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures (DIACFs) is generally associated with poor results because of secondary subtalar arthrosis and long-term changes in hindfoot morphology. Therefore, it has been argued that only an anatomic restoration of the articular surface and shape of the calcaneus can lead to better longterm results, and most surgeons are now in favor of surgical treatment. For an extended period, the gold standard in the treatment of DIACFs was open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) via an extended lateral approach. However, this approach was frequently associated with major wound healing complications (5.8%–43%) including hematoma, apical wound necrosis, superficial, and deep wound infections. In an effort to reduce these risks, minimally invasivetechniques were developed over the last several years, including percutaneous screw fixation, the sinus tarsi approach, the limited posterior approach, and arthroscopicassisted fixation. The sinus tarsi approach offers direct control of joint reduction without extensive soft tissue dissection and combined with percutaneous internal fixation, it offers a lower rate of soft-tissue complications. In this study, we aimed to assess the outcome of the sinus tarsi approach using percutaneous nail fixation rather than a plate for the treatment DIACFs. )
二、Objectives
评估经跗骨窦入路交锁髓内钉治疗移位的跟骨关节内骨折的疗效。 (To assess the outcome of the sinus tarsi approach and C-Nail fixation of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures (DIACFs). )
三、Patients
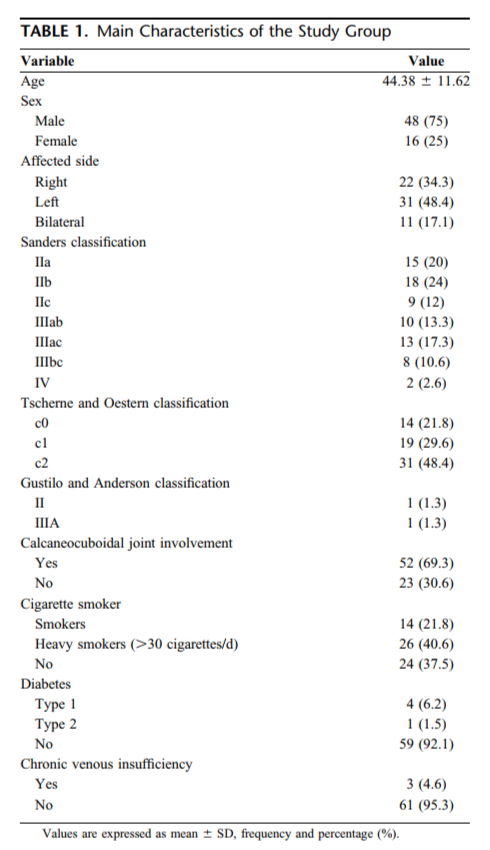
自2016-10-01至2018-12-31,共纳入64例(男48 女16)74足。
(Sixty-four patients (mean age 44.3 years, 48 men and 16 women) with 75 DIACFs were treated between October 1, 2016 and December 31, 2018. )
四、Intervention
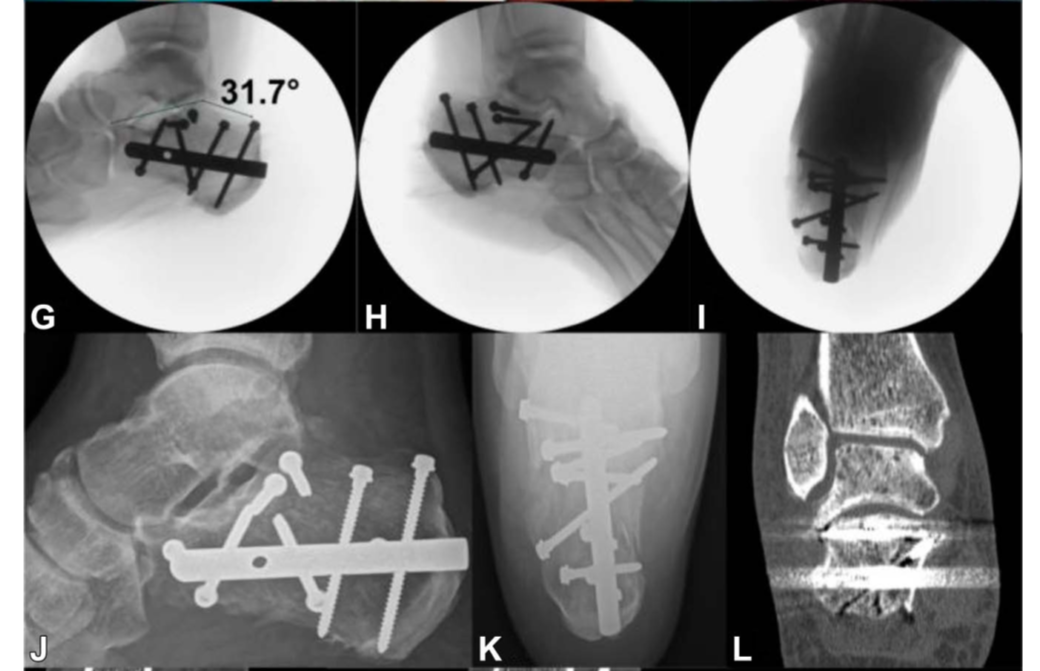
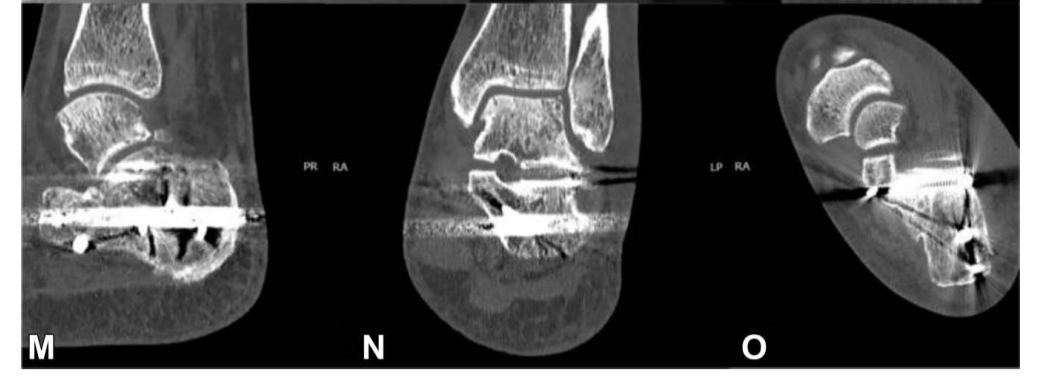
在所有病例中,后关节面通过跗骨窦入路,采用1-2枚螺钉固定。在所有关节的骨块固定后,采用经皮交锁髓内钉固定,6枚锁定钉。
(In all cases, the posterior facet was reduced through the sinus tarsi approach and fixed with one or 2 screws. After reducing all fragments to the articular block, the final fixation was performed percutaneously with C-Nail, locked with 6 screws. )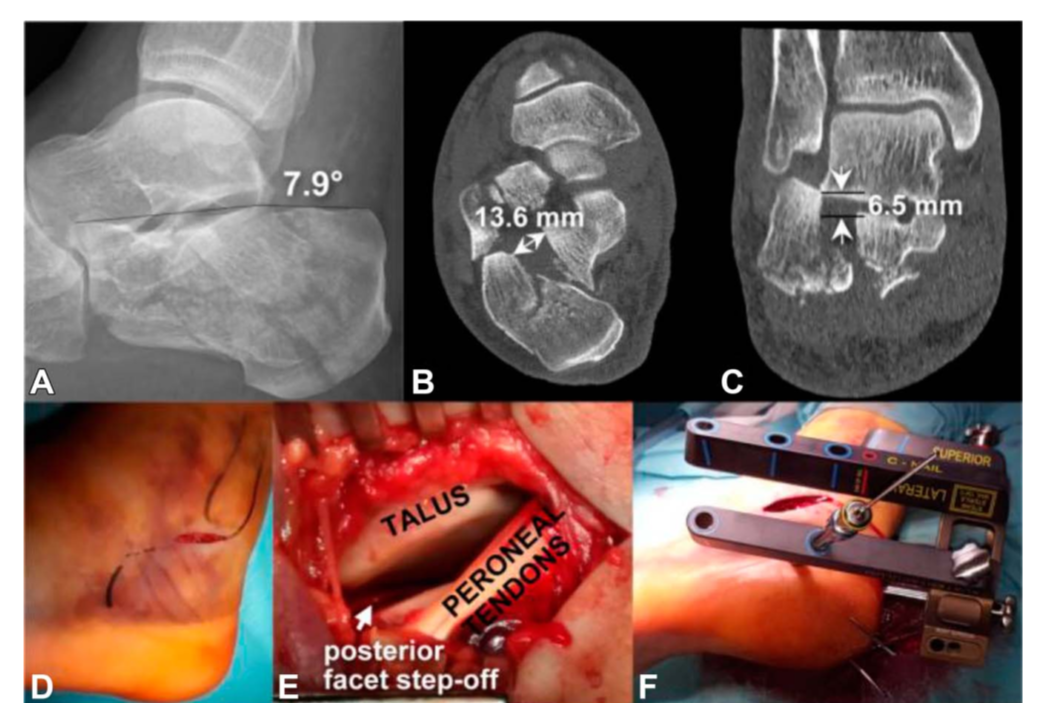
五、Results
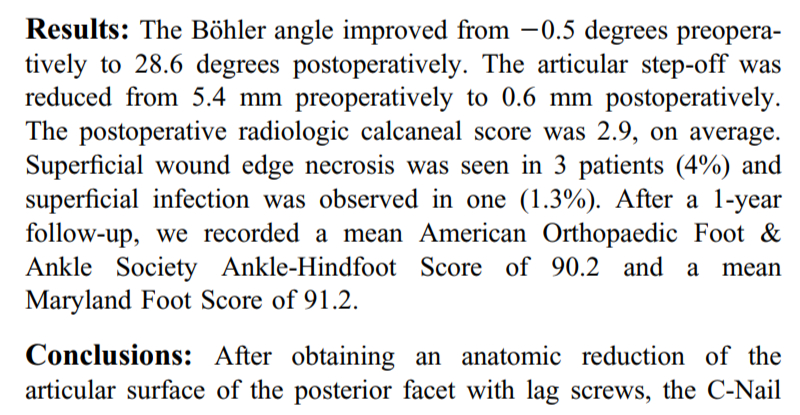
Böhler角由术前的-0.5°纠正到术后28.6°,关节面台阶由术前5.4mm纠正到术后0.6mm,术后影像学评分平均2.9。随后皮肤边缘坏死3例(4%),浅表感染1例(1.3%)。经过1年随访,平均AOFAS评分90.2分,平均Maryland后足评分91.2分。
(The Böhler angle improved from -0.5 degrees preoperatively to 28.6 degrees postoperatively. The articular step-off was reduced from 5.4 mm preoperatively to 0.6 mm postoperatively. The postoperative radiologic calcaneal score was 2.9, on average. Superficial wound edge necrosis was seen in 3 patients (4%) and superficial infection was observed in one (1.3%). After a 1-year follow-up, we recorded a mean American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society Ankle-Hindfoot Score of 90.2 and a mean Maryland Foot Score of 91.2. )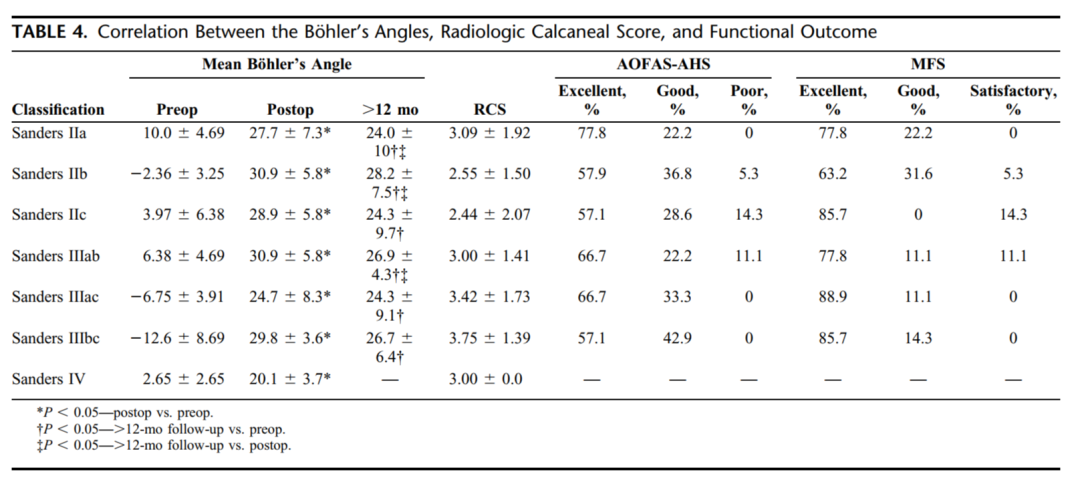
六、Conclusions
在后关节面通过螺钉获得复位后,交锁髓内钉可以作为移位跟骨关节内骨折具有较好的稳定性和低并发症的一种可选择的方法。
(After obtaining an anatomic reduction of the articular surface of the posterior facet with lag screws, the C-Nail represented a viable alternative to plate stabilization in the treatment of DIACFs, combining primary stability with low soft tissue complications. )



